Jiangjie Chen
Researcher
ByteDance Seed
Biography
Jiangjie Chen (陈江捷) is a researcher at ByteDance Seed Team. In 2024, he earned his Ph.D. at Fudan University in the School of Computer Science, Shanghai, China. His current interested research topics are mostly around building reasoning models and autonomous agents:
- Reasoning Models: Advancing research on incentivizing and understanding advanced reasoning and planning capabilities from large models.
- Autonomous Agents: Developing advanced methods for autonomous, trustworthy, and personalized agents. This extends towards the exploration of their interactions with multiple agents and real environments.
- Large Language Models
- Reasoning
- Mountaineering 🧗♂️
- Tennis 🎾
- Musicals
-
Ph.D. in CS, 2019 - 2024
Fudan University
-
B.S. in CS (honors), 2014 - 2019
Fudan University
News
-
Sept. 2025: Thrilled that our NeurIPS 2025 papers ARIA, KORGym, ORIGAMISPACE, and Enigmata were selected as Spotlight papers, and DAPO was selected for poster presentation!
-
Sept. 2025: Our papers Curse of Knowledge and LifeChoice are accepted to EMNLP 2025 Findings!
-
Jul. 2025: Our paper Past Meets Present won an Outstanding Paper Award at ACL 2025!
-
Jul. 2025: Check out our work on spatial cognition! Can LLMs Learn to Map the World from Local Descriptions? We demonstrate that LLMs can develop spatial awareness from fragmented local observations, successfully learning spatial perception and navigation in urban environments!
-
Jul. 2025: Check out ARIA! We propose a novel approach for training language agents with intention-driven reward aggregation. By projecting natural language actions into a lower-dimensional intention space, ARIA reduces reward variance and improves policy optimization, achieving 9.95% average performance gains across four downstream tasks.
-
Jul. 2025: Check out MemAgent! We introduce a novel approach to handling extremely long documents in language models through a multi-conv RL-based memory agent. MemAgent extends from 8K context to 3.5M QA tasks with <5% performance loss and achieves 95%+ on 512K RULER test!
-
May. 2025: Check out KORGym! We introduce a dynamic game platform offering over fifty games in textual or visual formats for interactive, multi-turn LLM reasoning evaluation with reinforcement learning scenarios. Our platform reveals consistent reasoning patterns within model families and demonstrates superior performance of closed-source models.
-
May. 2025: Check out Enigmata! We propose a comprehensive suite of puzzles for improving logical reasoning of reasoning models, tailored for RLVR training. We find that not only do such puzzles drastically improve puzzle reasoning of LLMs, but also improve SoTA models such as Seed1.5-Thinking on challenging reasoning tasks such as AIME and GPQA! This is a free lunch for SoTA models, since Enigmata is synthetic and can be generated at scale!
-
May. 2025: I was awarded with Nomination Award for Outstanding Doctoral Dissertation of Shanghai Computer Society!
-
May. 2025: Our papers DEEPER and HistoryAnalogy are accepted to ACL 2025!
-
May. 2025: Our paper CoSER is accepted to ICML 2025! Check out this comprehensive resource for role-playing agents!
-
Apr. 2025: Presenting Seed-Thinking-v1.5 from ByteDance Seed Team, a cutting-edge reasoning model that’s incredible in math, code, science, and logical reasoning!
-
Mar. 2025: DAPO is out! A new critic-free RL algorithm that directly trains a pre-trained base model to SoTA performance on AIME 2024 without any SFT.
-
Mar. 2025: Four papers accepted to NAACL 2025: SelfGoal, EvoAgent, EasyTool and Barrier in Language Agent Planning.
-
Oct. 2024: Three papers accepted to NeurIPS 2024 Workshop on Open-World Agents: EvoAgent, SelfGoal and AucArena. See you in Vancouver!
Experience
Awards
Featured Publications
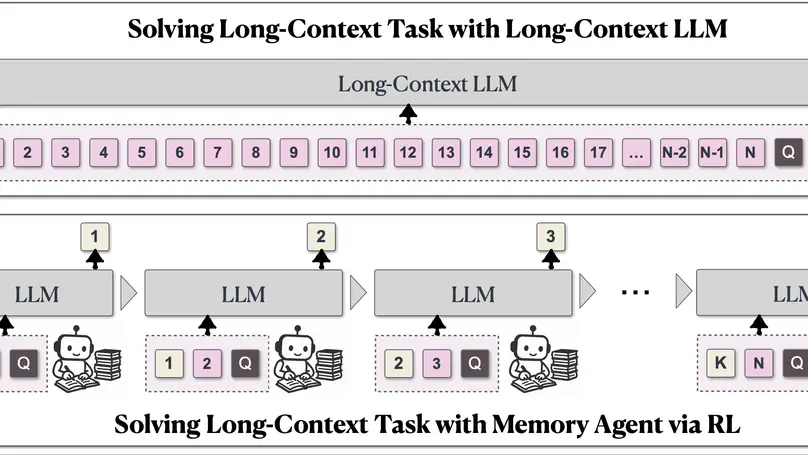
MemAgent introduces a multi-conv RL-based memory agent that enables language models to handle extremely long documents, extending from 8K to 3.5M tokens with minimal performance degradation.
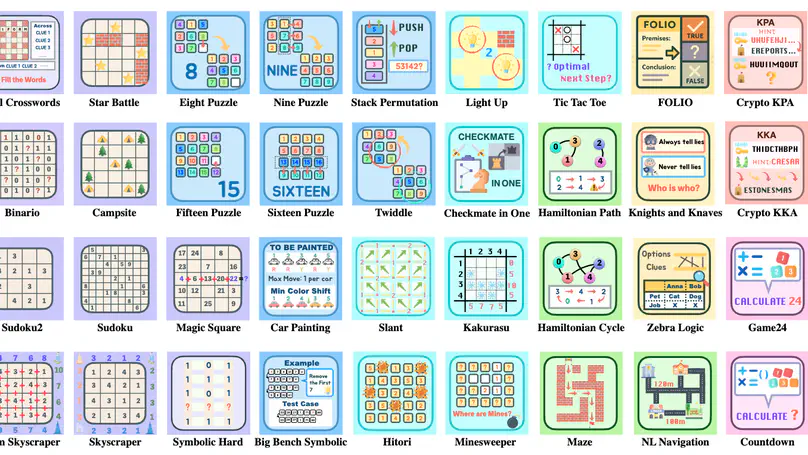
We introduce Enigmata, the first comprehensive suite tailored for improving LLMs with puzzle reasoning skills.
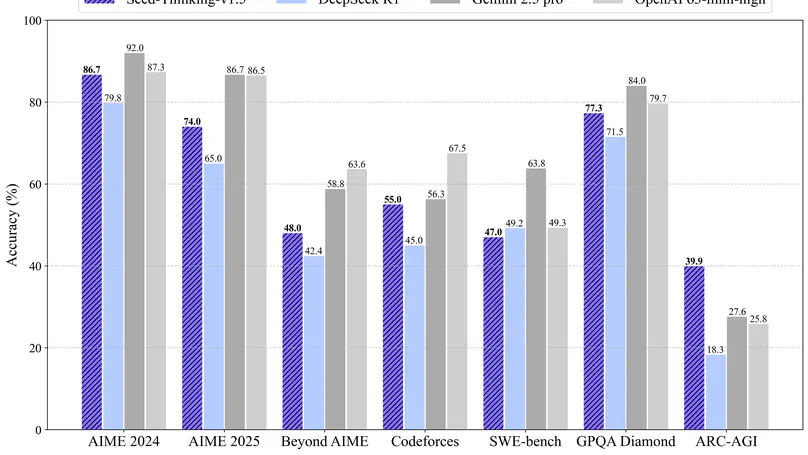
We introduce Seed-Thinking-v1.5, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model with a relatively small size, featuring 20B activated and 200B total parameters, capable of reasoning through thinking before responding, resulting in improved performance on a widerange of benchmarks.
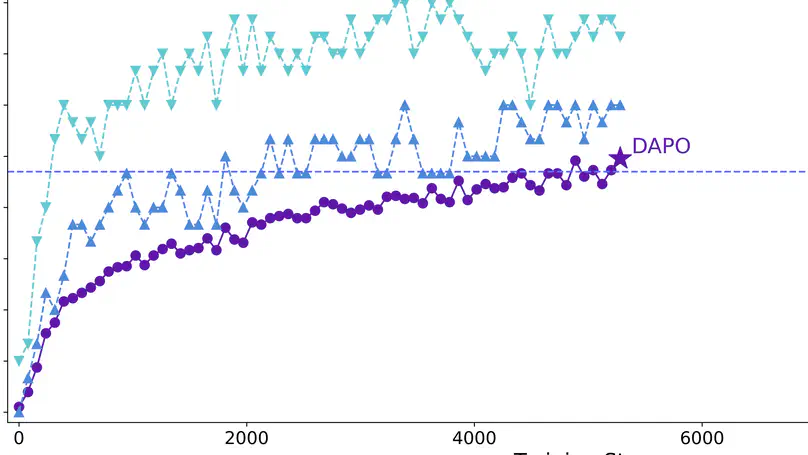
We introduce DAPO, a Decoupled Clip and Dynamic sAmpling Policy Optimization algorithm, and fully open-source a state-of-the-art large-scale RL system that achieves 50 points on AIME 2024 using Qwen2.5-32B base model.

We focus on acquiring historical analogies using LLMs, proposing a self-reflection method to reduce hallucinations and stereotypes, showing that LLMs have strong potential in this task.
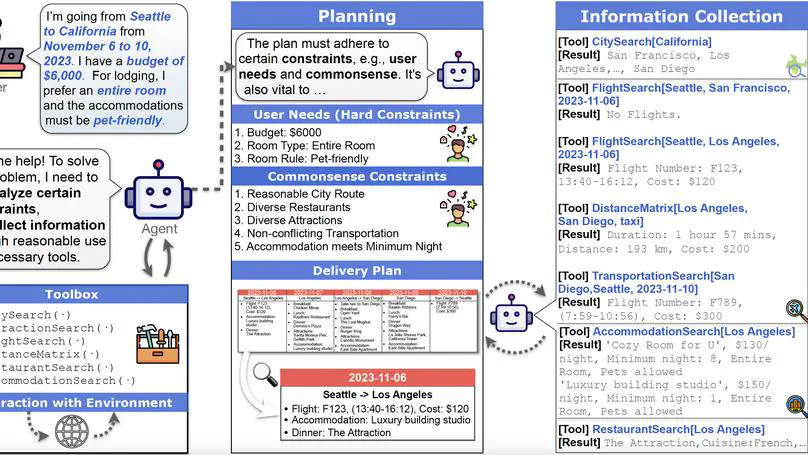
We introduced TravelPlanner, a benchmark for assessing language agents’ planning abilities, showing that even advanced models like GPT-4 face difficulties with complex tasks.

We present the first comprehensive and controlled investigation into the behavior of large language models when encountering knowledge conflicts.
