TimeArena: Shaping Efficient Multitasking Language Agents in a Time-Aware Simulation
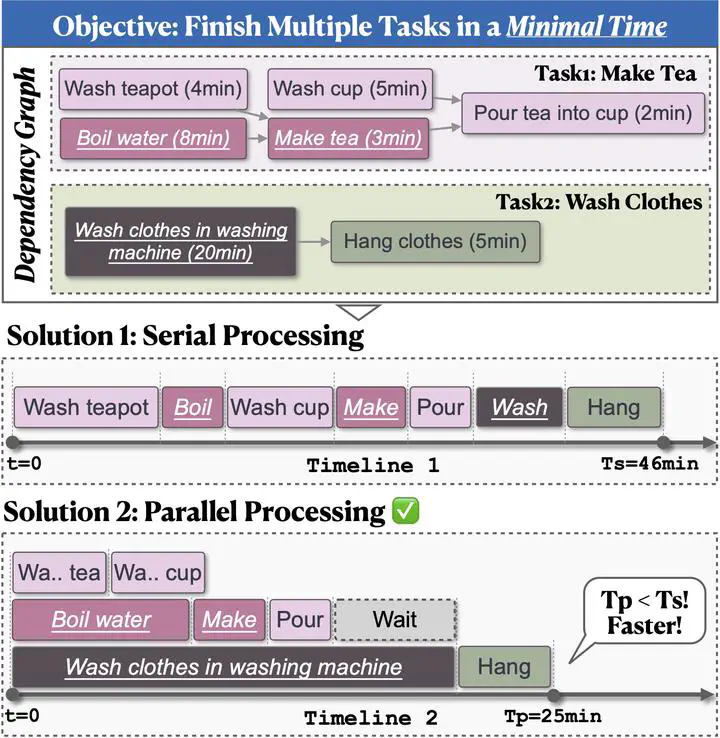 An example illustrating multitasking with temporal constraints in TIMEARENA. The completion of tasks requires actions in a predetermined dependency and order.
An example illustrating multitasking with temporal constraints in TIMEARENA. The completion of tasks requires actions in a predetermined dependency and order.
Abstract
Despite remarkable advancements in emulating human-like behavior through Large Language Models (LLMs), current textual simulations do not adequately address the notion of time. To this end, we introduce TimeArena, a novel textual simulated environment that incorporates complex temporal dynamics and constraints that better reflect real-life planning scenarios. In TimeArena, agents are asked to complete multiple tasks as soon as possible, allowing for parallel processing to save time. We implement the dependency between actions, the time duration for each action, and the occupancy of the agent and the objects in the environment. TimeArena grounds to 30 real-world tasks in cooking, household activities, and laboratory work. We conduct extensive experiments with various state-of-the-art LLMs using TimeArena. Our findings reveal that even the most powerful models, e.g., GPT-4, still lag behind humans in effective multitasking, underscoring the need for enhanced temporal awareness in the development of language agents.